Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) has moved from the drawing board to practical application for everything from customer service and healthcare to cybersecurity and robotics. Although still in its early stages, AI in cybersecurity has been at the center of this discussion as it becomes the shiny new toy for both security experts and cybercriminals.
What is artificial intelligence?
The term artificial intelligence invokes images of self-aware robots and computers running amok, but the reality of AI is much less dramatic. In plain terms, artificial intelligence combines computer science and large datasets to automate problem-solving and decision-making. Faster processing and high memory capacity have kickstarted the AI revolution we’re witnessing today. Important AI concepts include:
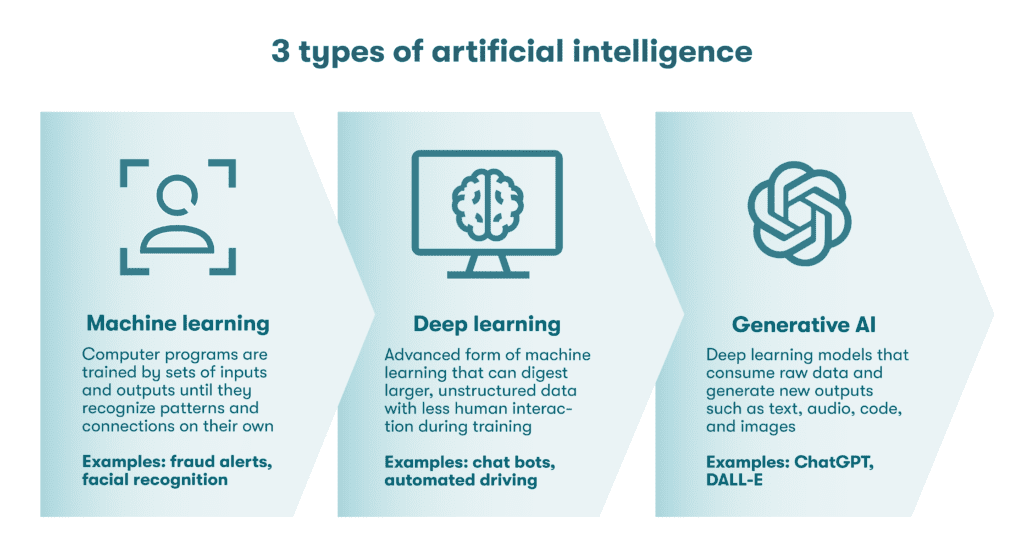
- Machine learning (ML) is the method used to train computer programs by feeding them sets of predefined inputs and outputs until they can recognize patterns and connections on their own.
- Deep learning (DL) is an advanced form of machine learning that can digest larger, unstructured data sets with less human intervention during the training process.
- Generative AI refers to deep learning models that consume raw data and generate new outputs that are similar to but slightly different from the original content, including text, audio, computer code, and images. Neural networks analyze complex patterns that can’t be deciphered by traditional machine learning.
Artificial intelligence has already been in practical use for decades for applications including translation services, robotics, and computer games, just to name a few.
Current uses of AI in cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity has also been with us for years. Security experts quickly leveraged the benefits of AI to sort large data sets and search for unusual patterns or malicious behavior. Current cybersecurity AI applications include real-time threat detection and response systems, risk management activities that analyze large volumes of data, and automated patch management. AI-driven security tools help quicken response times and reduce downtime.
With many companies processing over 1,000 security alerts each day, cybersecurity artificial intelligence is an effective way to ensure security issues are given the attention they deserve while preventing alert fatigue for IT teams.
Want to make life harder for scammers?
Check out our free username generator and random password generator tools.
Think you have a strong password? Use our password strength tester tool to put it to the test!
The benefits of AI in cybersecurity
As AI technology advances rapidly, the pros and cons of artificial intelligence are being discussed in classrooms, boardrooms, and even the halls of the US Congress. Is artificial intelligence a threat or a benefit? So far, AI has proven to be an asset for cybersecurity teams based on artificial intelligence advantages that include:
- High data capacity: The amount of data processed by company networks continues to multiply, which makes it difficult to manually monitor traffic and review network activities. The high data processing capacity offered by AI is a significant benefit, since it allows tedious data analysis, review processes, and 24/7 security monitoring to be offloaded without increasing security risks.
- Learning over time: Machine learning and deep learning processes allow cybersecurity software to learn from past experiences and improve over time. This ability to learn helps cybersecurity applications identify trends and connect the dots between past incidents and available threat intelligence. Deep learning algorithms can also analyze password patterns and trends to identify weak or easily guessable passwords and alert the relevant employees.
With the average person having 240 accounts to manage, no one has time to manually check all their passwords for vulnerabilities. An efficient way to review and improve your password safety is by understanding your Dashlane Password Health score.
- Improved threat detection: When AI-powered cybersecurity systems monitor networks and devices continuously, they can detect potential threats or signs of compromise in real time. AI can automate actions taken in response to a threat, like blocking malicious traffic, isolating devices, and sending out alerts to save valuable time and minimize the amount of compromised data.
- Reduced human error: Tedious, monotonous processes that are time-consuming and boring can also be subject to human error. AI reduces the chance of typos and formatting errors found in manually entered data sets and detects clues and anomalies in the data that human analysts might miss. Using AI in cybersecurity also reduces biases or preconceptions that humans might show while performing the analysis, although AI can still be subject to other sources of bias based on the nature of the data or algorithms used.
- Automated processes: Automation has become synonymous with artificial intelligence since the combination of data analysis and decision-making makes human intervention less necessary. Cybersecurity automation is key to 24/7 monitoring as well as streamlined patch management, compliance monitoring, and incident response processes.
- Accelerated troubleshooting: Troubleshooting issues quickly is essential, and AI in cybersecurity improves troubleshooting speed by using algorithms to assess incident severity and pinpoint what domain (which user, server, or network) the problem originated from. Automated analysis of log data makes it possible to determine the root cause and correct the issue quickly.
- Bot blocking capacity: Automated software programs (bots) are used to perform legitimate services like web indexing and customer support but can also be used by hackers for malicious purposes like distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks that overwhelm a website or network with traffic until it crashes. AI is a useful tool for recognizing and blocking bots based on behavior or IP addresses that are inconsistent with human behavior.
- Better user experience: Automated troubleshooting, monitoring, and incident response help to achieve the goal of more satisfied customers. Generative AI is moving to the front lines of customer support with features like interactive chat options to collect customer feedback more efficiently. AI is also improving the usability of many cybersecurity tools and features to improve their acceptance levels.
The limits of cybersecurity AI
Like most revolutionary technical advancements, artificial intelligence pros are balanced by a few cons. Concerns over AI deployment are based on weaknesses that include:
- Lacking human judgment. If AI possesses so much intelligence, why is human judgment still important? No matter how sophisticated cybersecurity AI becomes, the results will only be as strong as the data and computer algorithms behind them. Relying on AI entirely leaves the door open to unintentional biases and a lack of accountability that can detrimentally impact security and customer perception.
- Potential for false positives. A false positive is an alert that incorrectly indicates the presence of a vulnerability. This can happen when AI-based systems encounter new issues but lack the history or context needed to analyze them correctly. Too many false positives have the potential to overwhelm human IT teams or cause them to dismiss real threats in their midst. Automated reactions to false positives might also cause users or customers to be blocked unnecessarily.
- Can’t always keep up with new threats. Cybercriminals are revising their methods all the time, with the potential to outpace AI defensive capabilities. Cybersecurity artificial intelligence requires awareness and training data to prepare for the latest attack vectors. Hackers are constantly on the lookout for weaknesses like zero-day vulnerabilities that can be exploited before AI-based systems are prepared to address them.
- Ethical considerations. The widespread use of AI in cybersecurity and dozens of other applications raises ethical concerns. Privacy considerations, algorithmic bias, and job losses are among the ethical issues under discussion. Transparency in AI data collection practices helps to alleviate privacy concerns. The predictions for widespread job losses in cybersecurity may be unfounded since AI also creates new opportunities for IT professionals with relevant expertise.
- Cybercriminals are AI-savvy. In the ongoing cycle, cybercriminals have recognized the value of AI in creating new scams or enhancing existing ones. Automation contributes to DDoS attacks and credential-stuffing tactics that cycle through credentials in an attempt to gain unauthorized access. Some additional ways AI can be exploited for malicious purposes include:
—New malware strains created with the help of AI are more evasive and capable of evolving even after deployment to inflict greater damage.
—Phishing emails that attempt to trick unsuspecting recipients into providing personal information were once easily identifiable based on poor grammar and spelling, but generative AI can dramatically improve the quality and believability of these messages. - Cost considerations. Many AI-powered security solutions require specialized hardware, software, and technical expertise, making them cost-prohibitive for smaller organizations. As more security products integrate AI into affordable, cloud-based options, the benefits of AI should become more universally available.
Biometric authentication through fingerprint scanning or facial recognition is already built into most mobile devices. Discover how you can utilize these phishing-resistant, secure practices to access your Dashlane account easily with passwordless login.
References
- Investopedia, “Generative AI: How It Works, History, and Pros and Cons,” May 2023.
- Silicone Angle, “IBM debuts automated, AI-powered platform QRadar Security Suite to accelerate threat detection and response,” April 2023.
- Venture Beat, “5 ways AI-driven patch management is driving the future of cybersecurity,” May 2023.
- Field Effect, “Alert fatigue: 8 ways to avoid cybersecurity threat overload,” April 2023.
- The New Yorker, “Congress Really Wants to Regulate A.I., but no one seems to know how,” May 2023.
- Forbes, “How AI Is Disrupting And Transforming The Cybersecurity Landscape,” March 2023.
- Center for Internet Security, “What is Cyber Threat Intelligence?” 2023.
- Inside Big Data, “How AI Helps Prevent Human Error In Data Analytics,” March 2023.
- Risk Optics, “What is Cybersecurity Automation?” February 2023.
- Amazon, “What is a bot?” 2023.
- Dashlane, “Balancing Usability & Security in a Remote Office,” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “How AI Chatbots Like ChatGPT Could Impact Jobs,” February 2023.
- NIST, “False Positive,” 2023.
- Medium, “Pros and Cons of AI in Cybersecurity: Balancing Benefits and Ethical Concerns,” February 2023.
- Dashlane, “5 Key Cybersecurity Predictions Based on New Survey Data,” August 2022.
- Dashlane, “What the Hack Is Malware?” February 2020.
- Dashlane, “Why Dashlane Will Never Ask You for Credentials in an Email (Because That’s How Phishing Works),” November 2021.
- IBM, “What is artificial intelligence?” 2023.
- Ntrinsic, “The Impact of AI on Cybersecurity: Advantages and Disadvantages,” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “What Major Tech Companies Are Doing to Support Passkeys,” December 2022.
- Dashlane, “Introducing Passwordless Login For Dashlane,” 2023
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
