Modern, digital replacements for ID cards, passwords, and PIN codes have already arrived. Digital identity is improving authentication, simplifying computing and business practices, and creating a more level playing field for businesses around the world.
What is digital identity?

A digital identity (ID) is an electronic representation of information that can be used to positively identify a person. Much like conventional forms of identification, such as driver’s licenses and passports, a digital identity relies on information linked to one individual. Unlike physical IDs, a digital ID can be used to verify identity in both the physical and online realms. Digital identities are established based on:
- Unique attributes like date of birth, Social Security number, email address, and other individual identifiers.
- Credentials such as usernames, passwords, and biometric markers like fingerprints that can authenticate device owners when they use their digital IDs.
- Digital data that establishes user identification based on a user’s IP address, device information, and location.
Access controls use tools like digital identity certificates and secure online encryption processes to verify identity. Public encryption keys are provided to individuals based on attributes like their username or IP address, allowing them to access data or applications locked by corresponding private encryption keys until a positive identification is completed.
The key elements of digital identity
To better understand the purpose and importance of digital identity, you need to know why it’s being used, how it improves security, and how digital IDs can be safely controlled and distributed.
Usage
Instances of fraud and identity theft based on conventional ID formats have coincided with more online accounts for us to track and authenticate, each requiring a strong and unique password to gain access. Digital identification addresses these growing concerns by allowing individuals to authenticate themselves in a consistent, secure way, whether they’re logging in to a digital tool at work, boarding a plane, or entering a restricted facility.
Security
Digital identity improves security practices in many ways. The strong authentication process prevents unauthorized account access and helps businesses manage rights and permissions more easily. Digital IDs also improve online privacy and reduce the chances of identity theft based on stolen physical ID information. At the same time, digital identity minimizes fraud by making IDs nearly impossible to fake since they no longer rely on paper documents or cards that can be altered by hand.
Centralization
Centralization is an important element of digital identity since it allows the policies and procedures used to create digital IDs to be standardized and managed by one authority, like a large government agency or a trusted company. Centralizing also allows people to use the same digital identity for many different purposes because it steers everyone towards the same standard requirements and practices.
However, the notion of a centralized identity management system, perhaps on a global scale, also raises concerns. Centralization could make it more difficult for individuals to know how their information is being shared or used without their permission, such as through unwanted government surveillance or transferring of personal information between government agencies and private companies. Additional drawbacks of centralized digital identity might include:
- Computer errors that cause access problems to propagate across multiple accounts and applications.
- Overly invasive tracking and analysis of individual online behavior and physical movement.
- The implications of a cyberattack when all digital ID information is stored in one place and managed by a single authority.
5 benefits of digital identity use
The popularity of digital identification methods will continue to grow as more businesses and individuals experience the benefits, which include:
- Reduced risk of data breaches
Digital identity practices reduce the risk of data breaches because strong authentication protocols make it harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access. Digital identity solutions also monitor and log activity to detect suspicious activities in real-time. This allows companies or individuals to react quickly and minimize the impact of hacking attempts. - Less reliance on humans
Many of the weaknesses found in traditional identification methods are based on a reliance on humans, increasing errors. Digital identity automates authentication processes, making them more efficient and less error-prone. This also applies to the automation of individual processes like password generation and storage, where risky practices like password reuse undermine privacy and security by exposing multiple accounts during a breach. - Improved inclusivity
Digital identification creates a level playing field by removing some of the biases associated with physical IDs. Studies have shown that digital IDs improve access to healthcare, education, and jobs in countries that encourage their use and increase gross domestic product (GDP) by 3 to 13%. To experience such positive outcomes, digital identity systems must also be accessible to all and free from any biases or unfair restrictions of their own. - Ease of use
When you use a single set of credentials for multiple services, you no longer need to track and remember so many usernames and passwords, which makes your online activities easier and more efficient. Modern identification methods also build on the potential of biometric factors like facial recognition that are difficult to fake and don’t require plastic ID cards or identification codes. - Consolidation across different platforms
Consumers and businesses have always had to adapt to many different identity verification systems to complete their transactions. Digital identity creates a more standardized, centrally managed, and universally accepted system. Rather than entering your place of business with an ID card, unlocking your phone using facial recognition, then opening your email with a username and password, digital identity can eventually fold all these activities into one common platform.
Real-world use cases for digital ID
Digital identity isn’t a new concept, but modern technology has now taken universally accepted digital identification practices to new heights. Some useful and intriguing digital identity examples include:
Healthcare: Data privacy and patient identification are essential in the healthcare industry and form the basis of laws and regulations like HIPAA. Digital identity can be used to verify patients and doctors quickly before sending private healthcare data electronically. As remote care, like telemedicine, evolves, this improved authentication will also help preserve patient identity and confidentiality before and during virtual online visits.
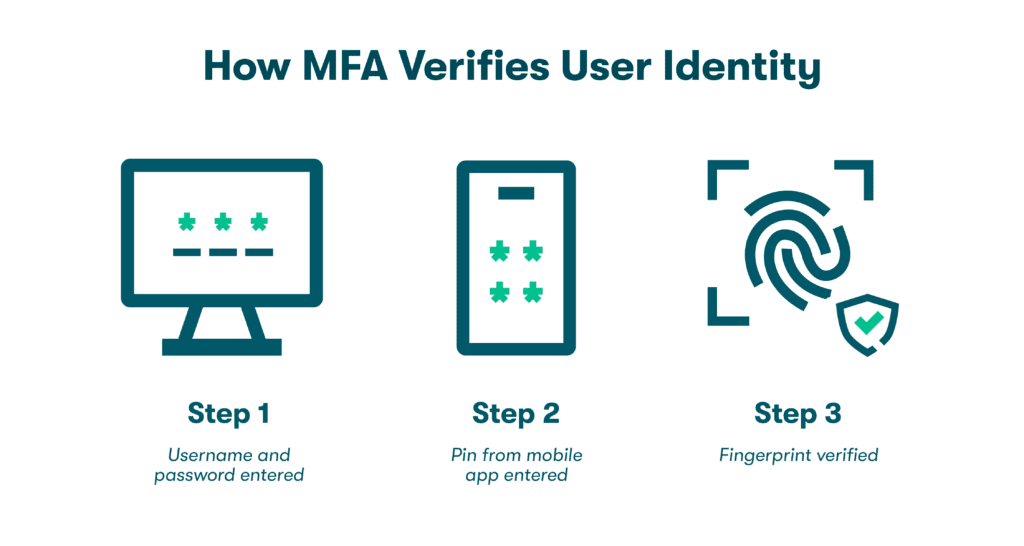
Government: Digital identity examples for government services include immigration processes that streamline identification at borders, fraud-proof voter registration, and heightened authentication practices to prevent tax or unemployment fraud. Most government websites already use 2-factor authentication (2FA) or multifactor authentication (MFA) to improve their cybersecurity, but digital identity spreads these security benefits across a wider variety of physical and online applications.
Finance: With the increased number of online deposits, fund transfers, and sales transactions, it’s no surprise that financial institutions are frequently targeted by hackers. When the identity of buyers and sellers can be verified in real-time, this reduces the chances of payment errors and cybercrimes. Digital identity and asymmetric encryption are also used to ensure cryptocurrency transactions can’t be altered or tampered with.
Employment: Verifying the identity and credentials of prospective employees can be a labor-intensive and time-consuming effort for human resource teams. With a common framework for identification established, employers can limit application fraud and screen candidates more efficiently. This verification process can even carry over to facility and system access using the same digital ID after the employee is hired.
The current trends and future of digital ID
The demand for digital identity is evident, with key trends pointing to widespread acceptance and adoption of these systems.
- More national digital ID initiatives
The coming years will see more digital ID initiatives at the state, national, and international levels. In 2021, the European Union (EU) launched a program designed to create secure digital identities for all Europeans, and other regions have established similar programs. These high-profile programs will speed up worldwide adoption. The United Nations has also called for universal digital identities by 2030.
- Digital licenses and IDs
Several U.S. states are now exploring or have already launched digital or mobile driver’s license programs. These digital IDs are already being issued in countries including Argentina, the United Kingdom, and Denmark. ePassports are also gaining momentum, with over 1 billion already issued by 150 countries. ePassports include a secure electronic chip with a parallel digital identity to prevent forgery and a biometric identifier in the form of a digital image.
- Greater demand for security and trust
Consumers, taxpayers, and voters are in favor of convenient online options, but not when they come at the expense of cybersecurity. Public demand for higher levels of security and trust is quickly moving us toward digital identity and guiding those who create the norms and practices.
- Commitment to privacy
Privacy is a must-have for the widespread adoption of digital identification. This starts with consent for the release of any information used to create a digital identity and includes safeguards to make sure this information isn’t shared. The zero-knowledge architecture used by security-first password managers is an example of how technology can be used to improve customer privacy.
Digital identity is a concept that brings together advanced cyber tools like multifactor authentication (MFA), data encryption, single sign-on (SSO), and secure information sharing to replace familiar physical IDs and create a universally recognized system for multi-purpose identification. These same advanced features, coupled with convenient password generation and autofill capabilities, make password managers indispensable.
Dashlane helps you generate and manage strong and secure passwords with ease. Standard features like AES-256 encryption, Password Health scores, 2FA, and a secure sharing portal improve your cybersecurity and productivity, while Dark Web Monitoring scans the depths of the internet for your credentials and alerts you if your password information is detected.
References
- Transportation Security Administration, “What are digital IDs and mobile driver’s licenses?” 2023.
- Fortinet, “What Is a Digital Certificate?” 2023.
- Dashlane, “How Strong Is Your Password & Should You Change It?” August 2022.
- Dashlane, “Webinar with Nicole Perlroth,” 2023.
- Okta, “The Importance of Centralized Identity Management,” February 2023.
- The World Identity Organization, “Digital identity: the good, the bad, and the – so far – unknown,” April 2022.
- The Sumsuber, “Blockchain, Digital Identity, and the Next Level of Data Security,” December 2022.
- Dashlane, “A Business Guide to Data Breaches and Hacks,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “How to Stop Reusing Passwords for Good,” January 2020.
- Security Boulevard, “How Digital Identification Could Be the Key to Inclusive and Economic Growth?” November 2022.
- Dashlane, “6 Things a Safe Username Should Always Do,” February 2023.
- National Library of Medicine, “Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act,” February 2022.
- Dashlane, “A Beginner’s Guide to Two-Factor Authentication,” August 2022.
- CyberPolicy, “What Type of Organizations Do Hackers Target the Most?” 2023.
- UNDP, “How digital can close the ‘identity gap,’” May 2022.
- Best Citizenships, “ePassports used by over 1 billion people for travels,” February 2021.
- Dashlane, “A Deep Dive into Dashlane's Zero-Knowledge Security,” June 2022.
- Dashlane, “Share your saved items in Dashlane,” 2022.
- Dashlane, “Dark Web Monitoring: Your Employees Are Likely Using Compromised Passwords,” July 2022.
- Dashlane, “Our Guide to Data Privacy,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “Putting Security First: How Dashlane Protects Your Data,” January 2023.
- Dashlane, “SSO Technology Overview & Integration With Dashlane,” September 2022.
- Dashlane, “Password Playbook for Healthcare Providers.”
- Dashlane, “Password Playbook for Financial Services,”
- Dashlane, “A Complete Guide to Multifactor Authentication,” November 2022.
- Dashlane, “What is Passwordless Authentication, and Why Should You Care?” November 2022.
- Dashlane, "Username Generator," August 2023
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
Related articles