Email Security Best Practices to Protect Your Business
Email became a widely used tool in just a couple decades. As email evolved into an essential business communication tool, it also became a source of security risks. Email security best practices combine advanced cybersecurity tools with training and education to protect businesses from email-related cybercrimes such as phishing and malware.
What is business email compromise?
Business email compromise (BEC) refers to any cybercrime or scam used to trick someone into divulging company information or sending money or data under false pretenses. The rise in remote work over the past several years has coincided with a rise in BEC incidents, with over 20,000 BEC complaints reported to the FBI in 2021 alone.
- Data theft: Email scammers are out to steal confidential information like trade secrets, HR data, or supplier lists that can be used to extort money or carry out additional scams. Business email security practices focus on educating employees and protecting business assets from hacks.
- Email account compromise: Business email compromise also includes cases where business email accounts are breached and taken over by the hacker. If you can’t log in to your business email account, notice email folders have been modified, or determine someone else has been sending business emails in your name, you should notify your IT department and change your email password immediately.
- Impersonation: BEC scams might involve impersonation of important company figures like IT team members, attorneys, or even the CEO. This social engineering strategy is easier to implement when an employee email account is breached, but a cybercriminal can also pull it off with spoofed email addresses that are similar to the real thing. The email scammer might make a request for money or data to be transferred under this guise of authority.

What is email security?
Email security is the practice of protecting email accounts from unauthorized access, compromise, data loss, and hacking. Secure email for business protects the company from threats like ransomware and spyware, which are frequently delivered through email messages. Business email security includes training and education to help employees stay informed on the latest email scams and tactics.
Want to learn more about using a password manager for your business?
Check out Dashlane's business plans or get started with a free business trial.
Why should you care about email security?
With over 300 billion emails sent and received each day, email has become the conduit for everything from informal exchanges to important contracts and documents. With email eclipsing physical mail, telegram, and fax as our medium of choice, focus has shifted to business email protection, which includes:
- Protection from data breaches and hacks: Studies have shown the majority of data breaches and hacks originate with an email. Email is chosen as a point of entry since it’s subject to human error and people’s trust in authority can be exploited. Although BEC impersonation schemes have decreased, the overall number of attacks continues to rise. Cybersecurity tools and training reduce vulnerability to common human errors.
- Compliance with data privacy laws: Businesses take steps to protect data privacy for both employees and customers. Data privacy laws are designed to prevent personal information from being shared without the owner’s consent. Without adequate data protection policies and practices, companies can’t ensure that emails for business purposes are secure from internal and external threats.
- Maintaining productivity: Email security helps minimize network downtime while reducing spam and other distractions. Rather than sorting through dozens of questionable (and potentially harmful) messages each day, employees can spend their time confidently reading and responding to legitimate communications.
- Protecting brand reputation: When email accounts are hacked, spoofed, or impersonated, the scam frequently extends to suppliers or customers. 76% of customers have made purchase decisions based on marketing emails. When the validity of these messages is questioned based on past security threats and incidents, brand reputations can suffer.
“Our strongest tools are our reputation and relationships. A breach could do more than take our security; it could remove the trust from our name that we’ve worked so hard to build.”
Principal, Vice President at JD+A
How to spot email threats
The best email protection starts with prevention, and technology alone can’t provide all the support. Learning to spot the signs of BEC and phishing is essential to reducing your vulnerability to cyberattacks.
- Unrecognized email addresses: Email threats can often be spotted based on minor changes to the domain name, such as one or two additional characters. The scammers realize these subtle changes often go uninspected or unnoticed and rely on this to get malicious emails past our defenses. Spoofed email addresses are used to deliver unsafe links or request private data.
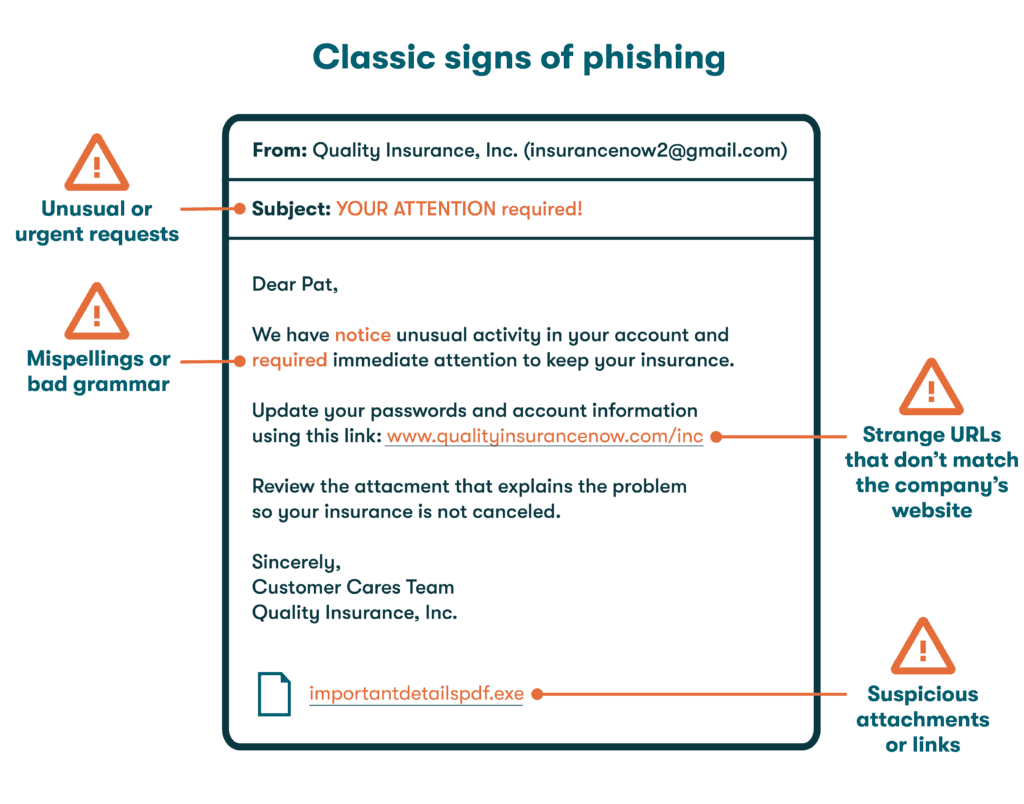
- Classic signs of phishing: The social engineering tactic known as phishing typically includes malicious email messages that appear to be from legitimate sources. These messages are intended to trick people into unknowingly providing information to a hacker. You can spot most phishing emails if you look carefully for:
—Unusual requests or a heightened sense of urgency.
—Strange URLs that don’t match the company’s website.
—Misspellings and bad grammar throughout the message.
—Suspicious attachments or links. A good email security best practice is to regard any embedded link as suspicious and type in the web address manually.
Best practices for email security
Email security for business can be heightened by remaining aware of the latest threats and paying close attention to the details. These email security tips and tools will also enhance your level of protection and help to keep your communications private.
- Set up a firewall. The network security devices known as firewalls filter all incoming and outgoing traffic and block suspicious files based on established security protocols. Hardware, software, or cloud-based firewalls can also be configured to screen incoming and outgoing email messages and block anything that appears to be spam or a phishing attempt.
- Use email security software. Email security software is available from many established vendors to help protect against phishing emails and other hacking attempts. The best email security software packages also scan messages to prevent prohibited data sharing, enhance email authentication processes, and scan attachments for malware.
- Turn on 2-factor or multi-factor authentication. 2-factor authentication (2FA) uses a second identifier, such as a code sent through an app, to verify the user. The extra seconds required to log in help prevent unauthorized email access that jeopardizes company security. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) uses two or more factors for the same purpose, and often incorporates biometric or passwordless authentication like facial recognition.
Passwordless login is a phishing-resistant alternative that instantly improves business email security. Passkeys and biometric technology are disrupting traditional hacking tactics and protecting us from social engineering and scams. Find out how we’re introducing passwordless login for Dashlane.
- Don’t use unsecure WiFi without a virtual private network (VPN). Learning how to keep your email secure requires identifying potential threats quickly. One such threat is unsecure public WiFi networks in places that can be subject to data intercepts, like airports and cafés. A VPN protects your email and other communications in public spaces by encrypting the data going into or out of your device and routing it through a secure portal. A VPN also masks your IP address so you can browse the internet privately.

- Use encryption. The centuries-old practice of encryption, or hiding information in an unrecognizable format, has become essential for password and website protection and is high on the list of best practices for email security. Encryption prevents emails from being tampered with in-transit to ensure the validity of the message and sender. Dashlane Password Manager utilizes AES-256 encryption, widely accepted as the strongest form of encryption available, to protect your passwords.
- Use a password manager. A password manager protects your email and other accounts by automatically creating strong passwords and storing them in a secure, encrypted vault. As you learn how to keep your email secure, a password manager helps you track, store, and share passwords safely to prevent email breaches and other cybercrimes that rely on stolen, weak, or reused passwords to gain access.
Password managers like Dashlane also include features like 2FA, a Password Health score, and Dark Web Monitoring for additional security. Automatic password generation features improve both security and convenience while eliminating the need to create and remember strong passwords for each account. Once your credentials are stored, the customizable Autofill feature will automatically warn you against entering credentials into the fraudulent website links commonly used in phishing scams. - Educate employees. With so many email security scams based on human error, psychological factors, and social engineering, employee training on email security is an essential element of an overall cybersecurity plan. Many companies use phishing awareness training, sending out simulated phishing emails to employees to test their knowledge and help them identify real threats. This real-world training can be reinforced by in-person or virtual training sessions and email security policies.
Businesses and employees are learning how to identify phishing attacks. However, there’s always more to learn and additional preventive steps to take. We break them down in Phishing 101: A Six-Step Action Plan.
References
- Microsoft, “What is business email compromise (BEC)?” 2023.
- Dashlane, “8 Hacker Protection Tips To Keep Your Online Accounts Safe,” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “What To Do If a Scammer Has Access To Your Email Address,” April 2023.
- Dashlane, “Twitter’s 200 Million-User Email Leak: What to Know and How to Protect Your Info,” January 2023.
- Microsoft, “What is email security?” 2023.
- Statista, “Number of sent and received e-mails per day worldwide from 2017 to 2025,” September 2022.
- Dashlane, “A Business Guide to Data Breaches and Hacks,” 2023.
- Tech.co, “75% of Cyberattacks Start With an Email, Report Says,” March 2022.
- Dashlane, “What Is Data Privacy & Why Is It Important?” April 2023.
- MailBuster, “Email Security Guide to Protect Your Brand’s Reputation,” 2023.
- Proofpoint, “What is Email Spoofing?” 2023.
- Dashlane, “Why Dashlane Will Never Ask You for Credentials in an Email (Because That’s How Phishing Works),” November 2021.
- Dashlane, “A Beginner’s Guide to Two-Factor Authentication,” August 2022.
- Dashlane, “Digital Identity 101: Everything You Need to Know,” April 2023.
- Dashlane, “What is Encryption?” March 2019.
- Dashlane, “7 Dangers of Sharing Passwords Without a Password Manager,” March 2023.
- Dashlane, “Dark Web Monitoring: Your Employees Are Likely Using Compromised Passwords,” July 2022.
- Dashlane, “5 Ways Dashlane Just Improved Its Autofill,” February 2023.
- Expert Insights, “The Top 11 Phishing Awareness Training Solutions,” April 2023.
- Dashlane, “Phishing 101: A Six-Step Action Plan,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks on Your Devices,” March 2023.
- Dashlane, “A Guide To External Security Threats in 2023,” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “Putting Security First: How Dashlane Protects Your Data,” January 2023.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
