5 Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Applications & Use Cases
Machine-to-machine (M2M) refers to the direct communication channels used to exchange information and perform tasks between machines without human intervention and with minimal supervision. While not essential, both artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can elevate the complexity of the tasks performed by M2M technology and enable it to be more autonomous.
The rise of M2M technology is a result of advanced modes of computing and connectivity, such as edge computing and 5G networks, both of which accelerate the exchange of data and information over the web. Nowadays, M2M is present in a wide variety of applications and use cases across multiple industries and markets.
Want to learn more about using a password manager for your business?
Check out Dashlane's password manager for small businesses or get started with a free business trial.
What is machine-to-machine technology?
Despite the name, machine-to-machine technology isn’t limited to hardware. It’s a combination of software, hardware, and network infrastructure that facilitates the transfer of data between machines.
An M2M system allows for separate machines to exchange information and collaborate on tasks without the manual assistance of a human. It can be used for a wide range of applications, from controlling climate in a conference room to autonomously implementing changes in a logistical operation, such as a supply chain, when unexpected events occur.
How does M2M technology work?
There are primarily two types of M2M devices for collecting and processing data. Data is generated in a collection of sensors and monitors that automatically transmit their findings to machines dedicated to processing the output. While the machine-to-machine communication can be wired, most rely on short-distance network coverage technology, whether it’s Bluetooth, WiFi, or RFID.
In addition to harvesting and processing data for insights, the machines are also able to send out instructions and adjustments according to the data they receive. In a factory setting, for example, an M2M network is able to automatically adjust factors such as temperature and humidity to keep them within a predetermined range.
When combined with AI or ML, the machines can even make “smarter,” more flexible decisions, instead of strictly following human-made instructions.
M2M vs. Internet of Things (IoT)
Functionally, there’s little difference between M2M and the Internet of Things (IoT). Machine-to-machine communication can be considered the predecessor to IoT, as it was first developed around 40 years prior.
Currently, the only concrete difference between the two technologies is that M2M devices can function without internet connectivity, relying instead on direct point-to-point communication. IoT networks, on the other hand, primarily feature machines that communicate through a shared cloud server.
M2M industry use cases
As an incredibly versatile technology, M2M has found its way into countless industries and sectors, especially with AI and ML allowing it to adapt to progressively harder challenges.
1. Industrial applications
Machine-to-machine communication can be used to monitor and automate highly complex and expansive supply chain and manufacturing operations. It allows machines, sensors, and controllers to exchange information in real time, making adjustments to the production process as needed, depending on the availability of resources and equipment.
M2M can be used to reduce the rate of human error, minimize collisions and bottlenecks, and increase worker safety.
2. Smart cities
Smart cities are a relatively recent application of M2M technology. Sensors are used to keep track of a city’s infrastructure and available public resources, such as parking lots, streets, public toilets, and trash cans. By tracking auto and pedestrian activity, smart cities can implement safer and more efficient traffic management and waste collection strategies in the long term.
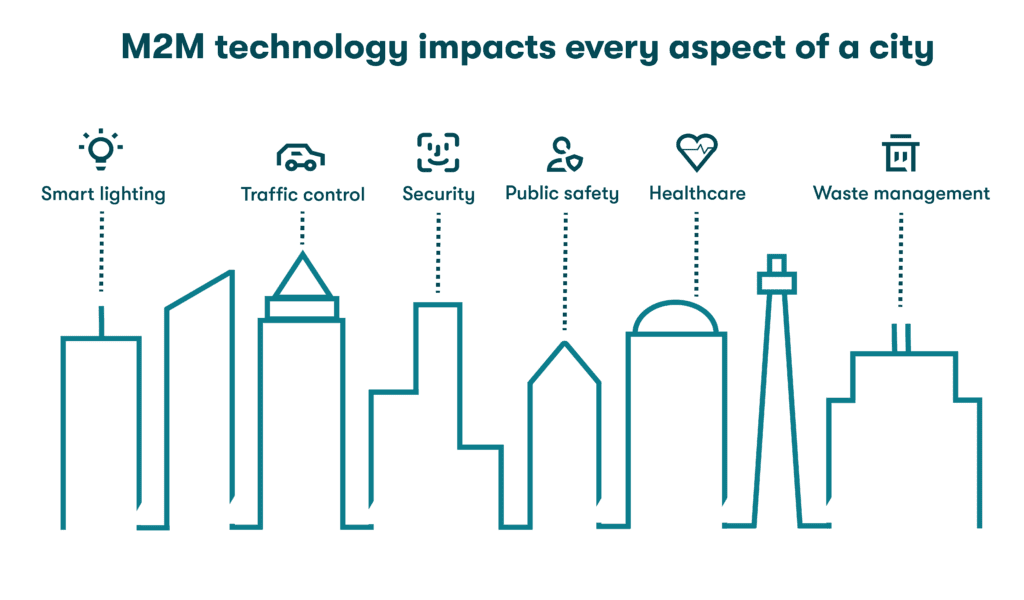
3. Consumer electronics
M2M technology isn’t limited to governments and large organizations. The same principles can be applied to making homes and office spaces smarter using connected wearables and environment monitoring.
The network can detect the presence of people in a specific space and adjust lighting, temperatures, and air quality accordingly while minimizing utilities in empty rooms to reduce energy consumption.
4. Healthcare
Whether it’s in a hospital or home care, M2M solutions are now used to directly transmit data of patients’ vitals to their primary care providers or specialists. By eliminating intermediaries and the human error factor, hospitals can minimize the likelihood of an attack on one of the most sought-after types of data by hackers. This can help boost the level of care available to patients while reducing strain on the healthcare system.
5. Finance
Taking advantage of wearables and digital wallets, M2M is used in digital banking. It allows customers to process payments automatically without needing to visit a dedicated sales register. This is not only more convenient for individual users, but organizations are also able to cut costs by minimizing their checkout and customer service staff.

Key features of M2M devices
Specialized M2M devices are necessary to utilize the technology to its full potential. There are multiple features you can expect to find in an M2M device, including:
- Reliable connectivity: Whether it’s wireless or not, connectivity is crucial for facilitating seamless data transmission between M2M devices.
- Security and access management: Encryption and access control mechanisms are vital for ensuring data integrity and maintaining secure communication within the M2M system.
- Continuous data exchange: The data sharing between M2M devices needs to be uninterrupted, as gaps in the data could lead to inaccurate or sub-optimal results.
- Real-time analytics: Data collected by sensors and wearables must be communicated to the rest of the M2M network in real time in order to support automated responses.
- Location and time-specific triggers: Some M2M devices need to be aware of their surroundings and timing, allowing them to optimize precision processes like supply chain management and fleet tracking.
- Low energy consumption: Since most M2M devices need to function around the clock, it’s important that they’re energy efficient. This not only ensures sustainability but also prolongs the life of battery-powered devices situated in hard-to-reach and remote locations.
Drawbacks of M2M communication
Despite its many benefits, M2M technology still has a few drawbacks that make it unsuitable for some applications:
- Strict security requirements: In-transit data is at its most vulnerable, so with M2M devices constantly exchanging potentially sensitive data, there must be strict security protocols in place, which can be complex and costly.
- Requires constant connectivity: Any interruption to the M2M device’s connectivity method can disrupt the communication between devices, leading to operation inefficiencies and gaps in data.
- Optimized for small networks: M2M solutions generally work best for smaller operations, as increasing the size results in connectivity issues and higher bandwidth consumption. Furthermore, upscaling can present a substantial increase in costs and potential errors due to the complexity of a larger network operation.
- Limited flexibility: A dedicated M2M system is usually designed for a specific task or industry application. This limits its adaptability to new requirements and makes upscaling more resource-intensive.
M2M security implications
M2M communication relies on numerous endpoints and devices, which can present a security risk for the network as a whole if not handled with care. M2M systems typically use access tokens to authenticate connections and verify the digital identity of an M2M device. A device is only given access to the network to transmit data and receive instructions if the authorization server has verified its access token.
There are a few additional ways you can protect your M2M system against unauthorized access, such as:
- Keeping software up-to-date
- Encrypting communication channels
- Restricting network access
- Employing firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Implementing a zero-trust security model
- Eliminating unused M2M devices
- Physically securing the M2M devices
- Using multifactor authentication (MFA)
Combined with AI, M2M solutions can phase out the need for human supervision and emergency interventions. Thanks to ML, M2M solutions can grow and adapt to protect a particular environment, learn to identify suspicious behavior, and respond promptly to attacks.
Enhance the security of your M2M technology with the help of machine learning, deep learning, and generative AI. Learn more about the applications and benefits of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity.
References
- Dashlane, “Hardware Security Key Purpose, Benefits & Use Cases,” September 2024.
- Analytics Steps, “Machine to Machine: Meaning, Key Features, and Communication,” August 2023.
- Freeway, “What is an M2M Connection?” February 2022.
- Particle, “M2M vs. IoT - Why You Need to Listen to What Your Machines Are Telling Each Other.”
- HowStuffWorks, “How the Internet of Things Works.”
- Plant Automation Technology, “M2M IoT Applications in Supply Chain and Logistics.”
- M2M Connectivity, “Smart City IoT Solutions.”
- NextPhase Medical Devices, “M2M Communication in Medical Device Development.”
- RF Wireless World, “Advantages of M2M Communication.”
- emnify, “What Is M2M Technology? The Power of Connectivity,” May 2023.
- Digital Guardian, “Data Protection: Data In transit vs. Data At Rest,” May 2023.
- Science Direct, “The challenges of M2M massive access in wireless cellular networks.”
- Stytch, “The complete guide to machine-to-machine (M2M) authentication and authorization,” December 2023.
- Dashlane, “A Complete Guide to Multifactor Authentication,” January 2024.
- Dashlane, “Putting Security First: How Dashlane Protects Your Data,” February 2024.
- Dashlane, “Why You Should Keep Your Apps Updated,” February 2024.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
