Two-Factor Authentication vs. Two-Step Verification: What’s the Difference?
Two-factor authentication and two-step verification sound so similar that most people assume they're two terms for the same type of security. Dig a little deeper, though, and you’ll find there are some key differences between the two. Here’s what you need to know about two-factor authentication vs. two-step verification.
What is 2FA?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an authentication method that requires a second credential from a different type of authentication factor.
An authentication factor is something a user knows, is, or has. As such, the three main types of authentication factors are:
- Knowledge: Ideally, knowledge-based factors are only known to the user. Examples include PINs and passwords.
- Biometric: Also known as inherence-based authentication, this factor is based on a user’s biological characteristics. Examples include fingerprints and facial recognition or Face ID.
- Possession: This type of authentication includes possession of an item, such as a mobile device or ID card.
While these are the main types of authentication factors, there are others as well, such as time-based authentication and location-based authentication.
2FA methods are designed to make it more difficult for unauthorized users to access an account, as they must provide two pieces of information from different authentication categories instead of one—for example, a password and possession of your mobile device with an authenticator app. Combining two types of factors for login helps block brute force attacks and dictionary attacks, as these hacking methods rely upon passwords only.
Want to learn more about using Dashlane Password Manager at home or at work?
Check out our personal password manager plans or get started with a free business trial.
Examples of 2FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is becoming increasingly common for websites and apps, but odds are, you’ve been using 2FA for decades without even realizing it. Common forms of 2FA you’ve likely come across in your daily life include:
- Push notifications: These are messages sent to a user’s mobile device or computer when they attempt to log in to an account. The user must then provide additional authentication by tapping an approval button within the message.
- Authenticator apps: These apps typically use time-sensitive codes to provide a second layer of security before logging in to an account.
- ATM transactions: ATMs require two pieces of authentication: A bank card and a PIN.
What is 2SV?
Two-step verification (2SV) is an additional layer of authentication that requires users to verify their identity at least twice when signing in to an account. Like 2FA, 2SV is designed to make it more difficult for unauthorized users to access accounts, but 2SV requires two steps in any type of authentication factor—even if they are the same type.
Examples of 2SV
Here are some real-world examples of 2SV:
- One-time PIN in email or text: After entering their credentials, users will receive a single-use link or PIN to enter in order to access an account. These aren’t the same as push notifications, as texts and emails are also protected by a password. Since the link or PIN is delivered via email or text, it's considered to be within the same authentication category (knowledge) as the initial password entered.
- Security questions: Users must answer one or more security questions before they can log in.
- Recovery codes: These are unique codes generated by a system when a password is forgotten, allowing a user to regain access to their account. Recovery codes are also referred to as temporary passwords.
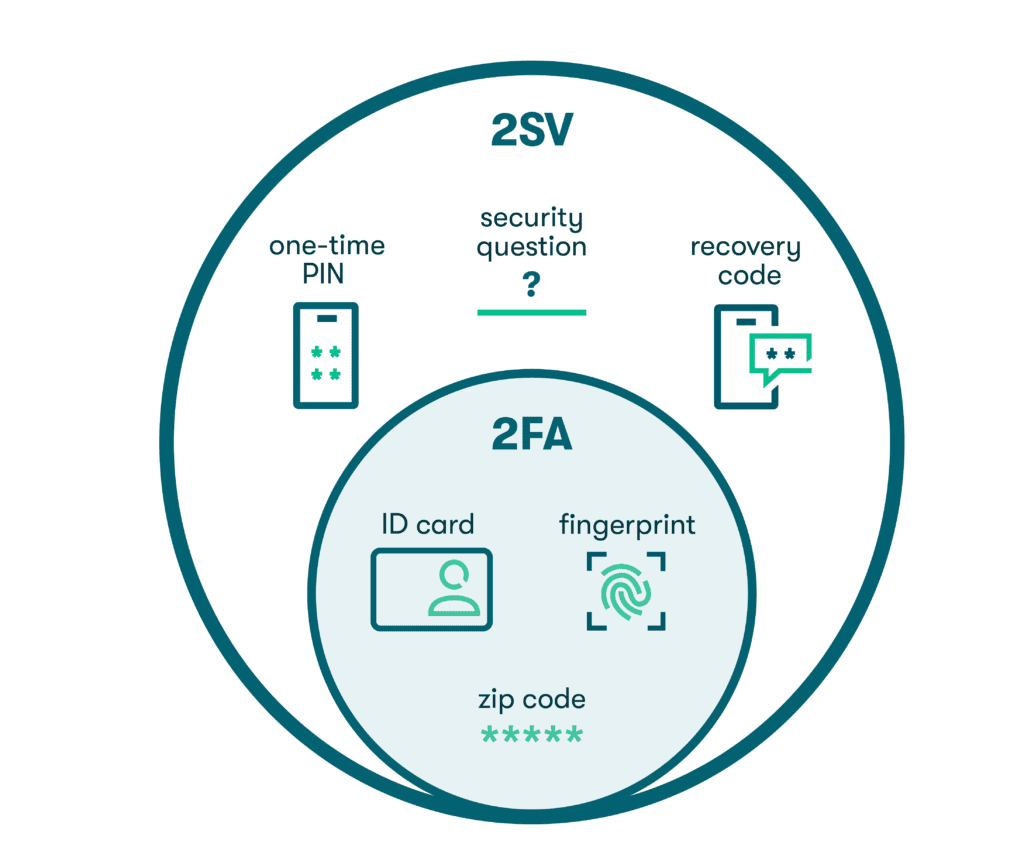
Differences between 2FA and 2SV
Just like every square is a rectangle, but not every rectangle is a square, every 2FA is 2SV, but not all 2SV is 2FA.
The key difference between 2-step verification vs. 2-factor authentication is that 2FA requires two independent forms of authentication from different categories. In contrast, 2SV only requires two pieces of information with no regard for whether they are from the same type of authentication category.
For example, a user logging into an email account may have to enter their password on their computer and then tap a confirmation via a push notification on their mobile device. This is two-factor authentication because it requires two independent methods from different categories (knowledge and possession). But if the user only had to enter their password and then answer security questions, this would be considered two-step verification—two pieces of information were required, but they were both knowledge-based authentication factors.
2FA is more secure, which is why it’s trusted in industries like healthcare, banking, and government. That said, both 2FA and 2SV can provide an added layer of protection to keep data and accounts more secure, and even 2SV is an improvement over simply entering a username and password.
Why 2FA is superior to 2SV
Two-factor authentication is a more secure alternative to two-step verification because it requires two independent pieces of information from different categories. This makes it harder for malicious actors to gain access to an account, as they must provide two forms of authentication that are not related, easily guessed, or possible to replicate. Using two different types of authentication factors is one of the best ways to prevent hacking, impersonation, and interception.
Many organizations rely on two-factor authentication to meet industry or government regulations and ensure their customers’ data is secure. It’s considered a best practice for businesses to use 2FA wherever possible—while consumers may view these additional steps as a minor inconvenience, they’re invaluable for protecting sensitive information.
Other security tips for verifying access
Aside from two-factor authentication and two-step verification, there are additional measures everyone should take to protect their online accounts:
- Create strong passwords for each account. A password generator is best. They create strong passwords that are difficult to guess, including a combination of numbers, symbols, and upper- and lowercase letters.
- Use a password manager. Password managers are one of the most effective ways to keep your accounts secure, as they store passwords for each of your accounts in an encrypted format.
- Don't fall for phishing attempts. Never open emails or click on links from suspicious sources. Phishing is becoming more sophisticated thanks to the advent of AI, but remember that no reputable organization will ask you for your own credentials.
- Opt for multifactor authentication when available. If you want to take 2FA methods to the next level, enable multifactor authentication (MFA). This requires users to provide multiple pieces of information from at least three different authentication categories before gaining access. When comparing two-factor vs. multifactor authentication, MFA is much stronger.
- Consider passwordless authentication. Passwordless authentication methods, such as biometrics, are becoming a popular alternative to two-factor authentication and two-step verification. These systems use biometric identifiers such as fingerprints and facial recognition to verify a user’s identity. You may already use this type of authentication to unlock your mobile device.
Rather than focusing only on verification vs. authentication, the best approach to online security is a multi-pronged approach.
How Dashlane uses 2FA to strengthen your privacy and security
Despite the clear advantages of 2FA, not all apps and websites have implemented this additional security feature. Luckily, Dashlane Password Manager secures and encrypts all of your account passwords in one place and supports 2FA.
Go passwordless with Dashlane for an extra layer of security. Learn how you can access your account with biometrics or a PIN code and leave behind the vulnerabilities associated with traditional passwords.
References
- Dashlane, “A Beginner’s Guide to Two-Factor Authentication,” August 2022.
- Wikipedia, “Time-Based Authentication.”
- Wikipedia, “Location-Based Authentication.”
- Dashlane, “How Dashlane Makes 2FA Easy,” June 2022.
- Dashlane, “From Maiden Names to School Mascots—The Best Ways to Use Security Questions,” September 2021.
- Dashlane, “A Complete List of PCI Password Requirements for Businesses,” June 2023.
- Whitehouse.gov, “Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity,” May 2021.
- Dashlane, “What the Hack is 2FA?” January 2020.
- Dashlane, “How Strong Is Your Password?” August 2022.
- Dashlane, “Why Dashlane Will Never Ask You for Credentials in an Email (Because That’s How Phishing Works),” November 2022.
- Dashlane, “MFA for Shared Accounts: Eliminate Security Risks,” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “What Is Passwordless Authentication and Why Should You Care?” November 2022.
- Dashlane, “Product Updates,” February 2022.
- Savvy Security, “What Is Two-Step Verification and How Does It Work?” August 2021.
- Software Lab, “What Is 2FA?” June 2023.
- IS Decisions, “MFA vs 2FA vs 2Step: How to Choose the Right Multi-Factor Authentication?”
- Dashlane, “Don’t Get Hooked: Dashlane Celebrates No Phishing Day,” June 2022.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
